On February 20th, Advanced Science published online the latest genetic and functional modification of therapeutic T cells against cancer made by the team of Professor Yang Guang, College of Life Science, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, in collaboration with Professor Ouyang Suny, Fuwei Hospital.
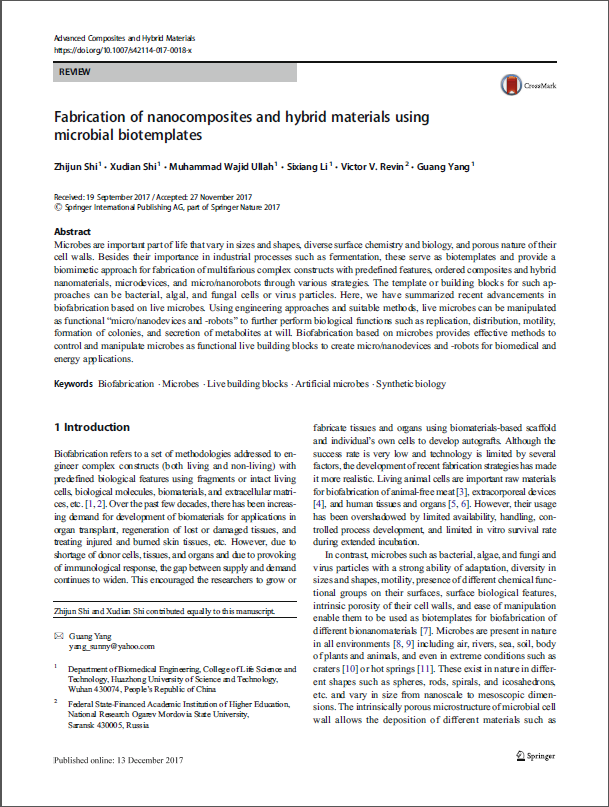
Car-t cell therapy is a new type of tumor immunotherapy following surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy (Figure 1).
At present, positive clinical effects have been achieved in the treatment of B-cell malignant tumors, but there are still some problems, mainly related to the preparation of CAR-T cells, safety and therapeutic efficacy against solid tumors.
So we need to design new methods to produce more effective cars and give them the ability to track their anti-tumor efficacy in CAR-T therapy.
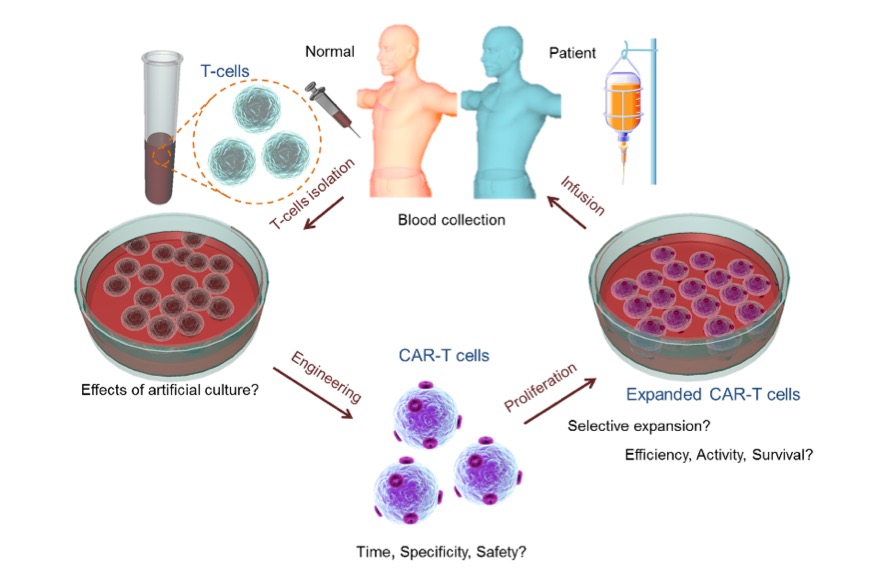
Figure 1 schematic diagram of the main flow of CAR-T therapy
Due to a lack of appropriate targets, cytokine storm, in vitro neurotoxicity and preparation of such problems as high risk and high cost, CAR - T therapy in the treatment of most except B cell tumor in malignant tumor is still a long way, especially for the treatment of malignant solid tumor, due to the physical barrier of dense tissue and microenvironment of immunosuppression, CAR - T cells in tumor tissue penetration, immune activity have been greatly restricted.
The review on the discussion of the CAR - T therapy limitations, on the basis of systematically summarizing and nanotechnology in enhancing immune cell therapy were reviewed, especially the CAR - T therapy for tumor precise treatment of the main strategies and application status (figure 2), introduced by the design of functional nanoparticles enhanced CAR - preparation, proliferation of T cells, transportation, targeted, activation and detect important advances, mainly includes the following aspects: 1) as a carrier of gene transfection in vitro and in vivo preparation CAR - T cells;
2) Promote T cell amplification and persistence;
3) Improve T cell transport;
4) Promote the intrinsic T cell activity;
5) Recombinant immunosuppressive cells and vascular microenvironment;
6) Monitor the efficacy of CAR-T therapy.
Functional nanoparticles auxiliary CAR - T therapy combined with the advantages of nanotechnology and CAR - T T therapy in overcoming the CAR - limitation, improve the curative effect has achieved initial results, is rapidly becoming a CAR - T therapy basis and clinical translational research is an important new direction, to a CAR - T attack more, including solid tumor, malignant tumor therapy provides a powerful and effective strategy.
Finally, some important common problems such as efficiency, safety, transformation potential and possible solutions are analyzed and prospected.
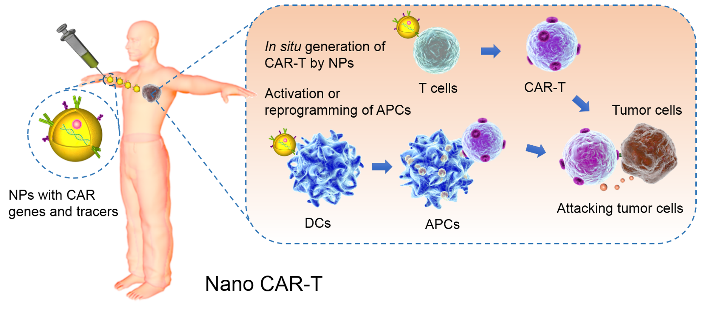
Figure 2 Nanotechnology assisted immunocell therapy for precision tumor therapy
Postdoctoral fellow Ahmed M. E. Abdalla and Dr. Xiao Lin are co-first authors of the paper, and Dr. Xiao Lin, Professor Ouyang Chenxi and Dr. Yang Guang are co-corresponding authors of the paper. The research work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The thesis links: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.201903164