A study of finasteride /PHBV/ POLYvinyl alcohol/chitosan "drug storehouse" microspheres as potential embolization agents
Professor Yang guang at life college team and huazhong university of Science and technology professor of tongji hospital orthopedic XiaoJun teamwork in biological materials authoritative journal the journal Biomateirals Science entitled "Development of finasteride/PHBV @ polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan reservoir -type microspheres as a potential embolic agent:
Vitro from in vitro evaluation to Animal study.
Prostatic artery embolization has become a mature and safe and effective method for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
However, there are few reports on the use of drug - loaded embolization agents in the treatment of prostatic artery embolization.
In recent years, "drug bank" composite microspheres, a continuous polymer matrix containing multiple drug delivery carriers, have been used in a controlled manner to extend the duration of drug action.
In this study, we first adopt the prepared emulsion solvent evaporation method of load finasteride poly hydroxybutyrate valerate (PHBV) microspheres, and then through the antiphase suspension crosslinking method will take drug microspheres coated with poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan polymer matrix, the preparation of finasteride/PHBV/poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan microspheres "pharmacy" type system.
The average diameter of the microspheres was 238.1 ± 27.3 m.
Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan polymer matrix contains multiple PHBV microspheres.
Delayed the sudden release of the drug, and the release time reached 51 days.
In vitro biocompatibility studies showed that the microspheres had no obvious cytotoxicity and had good blood compatibility.
In addition, embolization of the central auricle artery in rabbits showed that the microspheres could induce progressive ischemic necrosis of the rabbit ear tissues, and histopathological sections showed that fibrosis occurred around the embolized microspheres, with less inflammation.
Further observation of the ultrastructure of the vascular endothelial cells in the central auricular artery of rabbits showed that the endothelial cells had nuclear deformation, chromatin deepening, mitochondrial swelling or vacuoles and other morphological changes after microsphere embolization.
These results suggest that the compound drug-loaded microspheres could be a potential drug delivery system for the embolization treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The first unit of this paper is School of Life, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. The co-authors are Li Xiaohong, a doctoral student in School of Life, and Ji Xiongfa, a doctor in Tongji Hospital. The corresponding authors are Yang Guang, a professor in School of Life, and Xiao Jun, a professor in Tongji Hospital.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21774039, 51603079, 31270150).
Link to paper:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/BM/C9BM01775E#!divAbstract
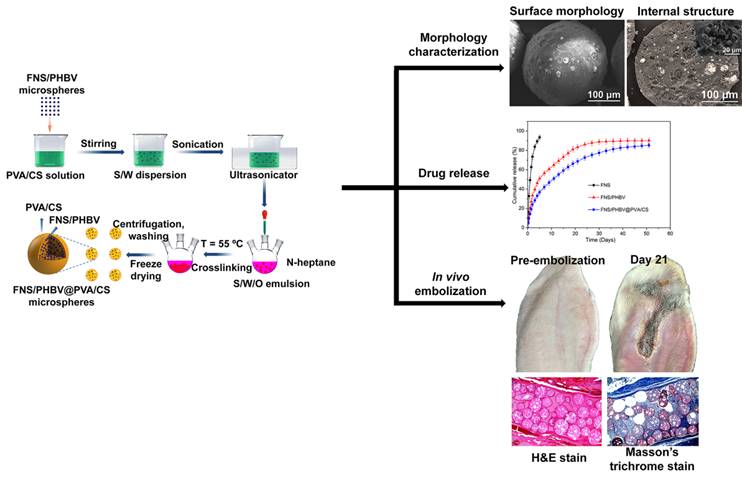
Preparation, structure characterization, drug release and rabbit ear embolization of finacystalline /PHBV/ POLYvinyl alcohol/chitosan "drug storehouse" microspheres