[Research Trends] Professor Yang Guang's team, School of Life Sciences, Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Based on the effect of hydrogel coupled electric field of regenerated bacterial cellulose on cell proliferation
-Carbohydrate Polymeric Stimulation Based on Electroactive was published on 22 July 2020 in the international journal of Carbohydrate Polymers
Research paper of Regenerated bacterial cellulose Hydrogels ".
Effective wound healing still faces great challenges, and the existing treatment methods, such as sterile wound dressings, negative pressure, ultrasonic treatment, etc. are expensive, time-consuming and need to be further improved.
In recent years, in vitro electrical stimulation has played an important role in promoting wound healing under the effect of simulated biological endogenous electric fields.
However, electrical stimulation alone is not sufficient to cover the entire wound and the electric field is not stable.
Based on these questions, the research team developed a biocompatible conductive hydrogel based on regenerated bacterial cellulose (rBC) and explored the effects of coupled electrical stimulation on cell activity for application in wound healing.
The research team firstly prepared bacterial cellulose (BC)/polypyrrole (PPy) films by in-situ composite method, then dissolved BC/PPy and physically doped carbon nanotubes (CNT) through sodium hydroxide/urea solution, and finally prepared rBC/PPy/CNT conductive hydrogel by physicochemical double-crosslinking method.
The conductive hydrogel has good thermal stability, mechanical strength, compression resistance, swelling and electrical conductivity.
In vitro biocompatibility studies showed that hydrogels had no obvious cytotoxicity and could promote cell growth well.
In addition, when rBC/PPy/CNT hydrogels were coupled with electrical stimulation, cell proliferation was found to be significant.
These results suggest that the composite conductive hydrogel coupled electrical stimulation can be applied in tissue engineering as a potential system to promote wound healing by enhancing cell activity.
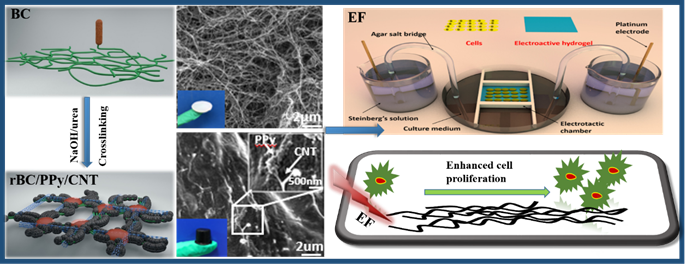
FIG. 1 Schematic diagram of rBC/PPy/CNT coupled electrical stimulation on cell proliferation
The first author of this paper is Wang Li, PhD student, School of Life, Huazhong University of Science and Technology; Professor Yang Guang, School of Life, Huazhong University of Science and Technology; and Dr. Shi Zhijun, School of Life, Huazhong University of Science and Technology are corresponding authors; and Huazhong University of Science and Technology is the first author unit.
The research work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key Research and development Plan.
The thesis links: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116829
Paper Citation:
Li Wang, Sanming Hu, Muhammad Wajid Ullah, Xiaohong Li, Zhijun Shi, Guang Yang, Enhanced cell proliferation by electrical stimulation based on Electroactive regenerated bacterial cellulose Hydrogels,
Carbohydrate Polymers, Volume 249, 2020, 116829, ISSN 0144-8617, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116829.