-
Article: Applications of super hydrophobic liquid-solid friction nanogenerators as droplet sensors in biomedicine In recent years, friction nanogenerators have become the focus of attention of rese...2020 - 08 - 23
-
[Research Trends] Professor Yang Guang's team, School of Life Sciences, Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Based on the effect of hydrogel coupled electric field of regenerated bacteria...2020 - 08 - 19
-
July 9, 2020Bricard and clemence, international students in 3-Bio research group, successfully completed their master thesis defense.The silhouette of the international student BricardThe silho...2020 - 07 - 18
-
On February 20th, Advanced Science published online the latest genetic and functional modification of therapeutic T cells against cancer made by the team of Professor Yang Guang, College of Life Sc...2020 - 07 - 15
-
According to the Regulations of Huazhong University of Science and Technology on the Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements, the following is the publication on the transformat...2020 - 07 - 10
-
Prof. Guang Yang’s group makes progress in self-healing hydrogels and wound healing18 June 2020,a research paper by Prof. Guang Yang’s group entitled“Rapid fabrication of self-healing, conducti...2020 - 07 - 01
-
"Learning in Epidemic" series of cloud report, let the teachers and students better charge during the epidemic -- Yang GuangProfessor Yang Guang is a professor of biomedical engineering in the Scho...2020 - 06 - 30
-
Synthesis of bacterial cellulose based on solid-gas-liquid interfaceBacterial Cellulose (Bacterial Cellulose, BC) is a kind of consists of gluconic acid bacilli in the process of growth of synthe...2020 - 06 - 28
-
Combining silk sericin and surface micropatterns in bacterial cellulose dressings to control fibrosis and enhance wound healingBiaou O. Ode Boni, Lallepak Lamboni*, Bianza M. Bakadia, Saied A. Huss...2020 - 06 - 28
-
A study of finasteride /PHBV/ POLYvinyl alcohol/chitosan "drug storehouse" microspheres as potential embolization agentsProfessor Yang guang at life college team and huazhong university of Science ...2020 - 06 - 28
-
Water-stable and finasteride-loaded polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous particles with sustained drug release for improved prostatic artery embolization — in vitro and in vivo evaluationProfessor Yang G...2020 - 06 - 27
-
My beautiful encounter with China, Wuhan and HUSTBeauty of China, beauty of HUST My name is Abeer and my Chinese name is 韩美. I fall in love with my Chinese name because it has 美, which represent...2020 - 06 - 27
-
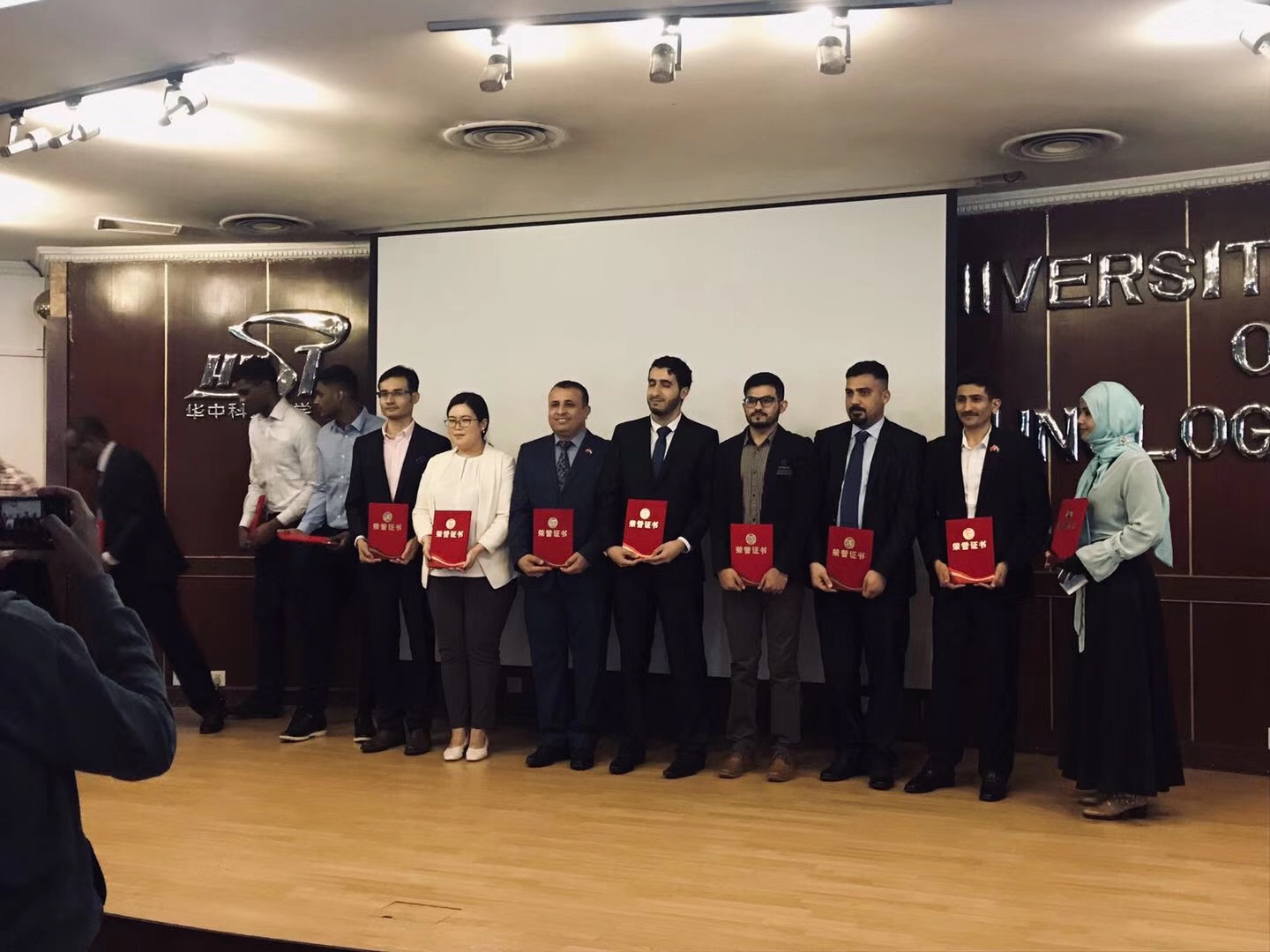
On May 16th, the Huazhong University of Science and Technology Excellent International Student Recognition Conference was held at the International Exchange Center. Eight of the 3BIO team students ...2019 - 07 - 14
-
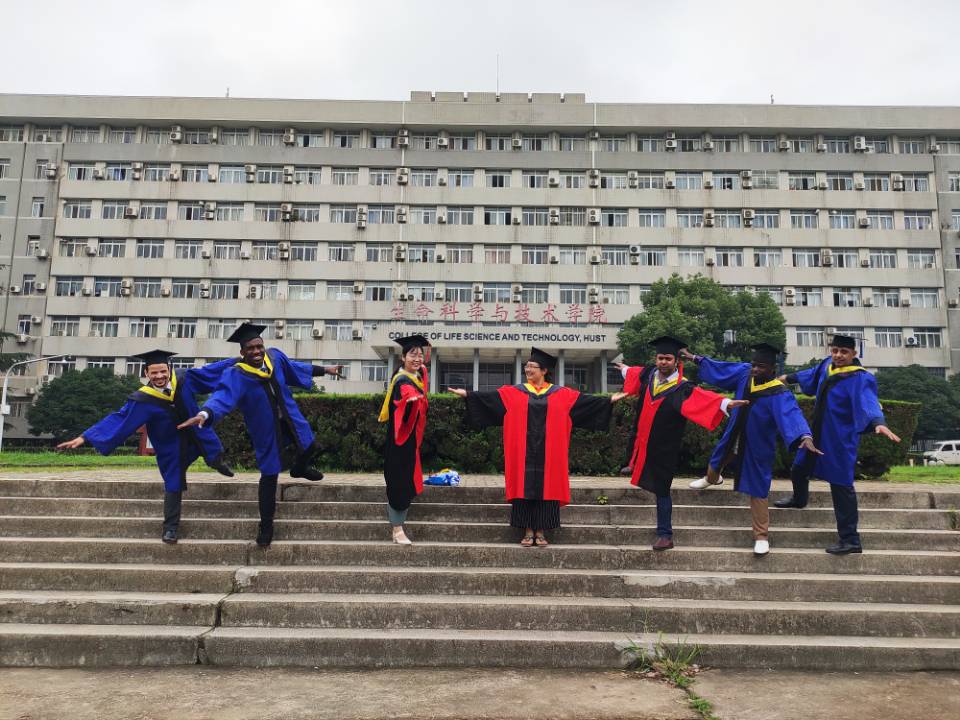
On May 20th, Raju, a Ph.D. student of the research group, completed his doctoral graduation and completed his four-year study abroad in China. On May 14th, the master student Yin Yaqi and the inter...2019 - 07 - 09
-
Bioinspired Materials Science and Engineering (ISBN: 978-1-119-39034-3, Chinese translation: Biomimetic Materials Science and Engineering) was officially published by Wiley, Professor Yang Guan...2018 - 09 - 04
-
The group published an article in the journal Advanced Composites and Hybrid MaterialsZhijun Shi1 & Xudian Shi1 & Muhammad Wajid Ullah1 & Sixiang Li1 & Victor V. Revin2 & Guang Yang1Received: 19 Se...2017 - 12 - 20
-
Professor Yang Guang visited UPM University at the invitation of Dr.Hidayah Ariffin, Executive Chairman of the General Assembly, and invited the report2017 - 11 - 27