Self-powered flexible electromagnetic sensors based on flexible magnets are promising to be applied in wearable field. As the core component of motion sensors, flexible magnets require excellent mechanical and sensing properties. However, most reported flexible magnets were fabricated with non-degradable substrate materials via complicated processes which leads more serious pollution. Meanwhile, the non-contact type of flexible electromagnetic sensors is able to work in some harsh conditions.
Recently, Professor Guang Yang’s 3Bio Group at College of Life Science and Technology, Professor Bin Su at Materials Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology reported a novel flexible, biodegradable and self-powered electromagnetic sensor as the title of CoFe2O4 Embedded Bacterial Cellulose for Flexible, Biodegradable, and Self-powered Electromagnetic Sensor based on CoFe2O4-embedded magnetic bacterial cellulose in the international journal of NANO ENERGY.
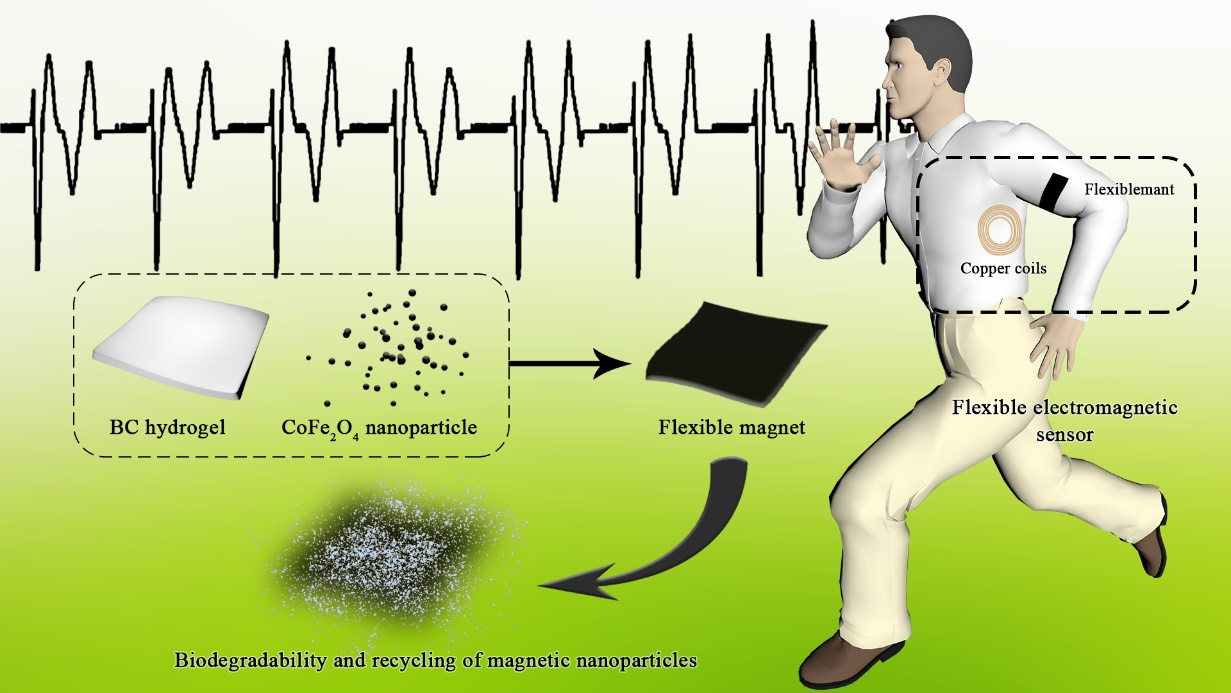
The flexible, biodegradable and self-powered electromagnetic sensor was prepared based on CoFe2O4-embedded magnetic bacterial cellulose, which is prepared by a facile and economical in-situ co-precipitation paired with a post-process of hot-pressing and magnetizing. Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles were synthesized in network structure of degradable bacterial cellulose for flexible composited magnetic films. Degradation experiment demonstrated that the flexible magnetic films degraded completely within 56 hours, and the left magnetic materials of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles could be recycled. Compared with nano-generator sensors and stress-strain sensors, the non-contact type of flexible electromagnetic sensors avoids the abrasion and damage from touch. In platform sensing test, the flexible electromagnetic sensor exhibits excellent stability (signal attenuation lower than 4% over 1000 cycles) and during the sensing performance test, the peak voltage was able to be adjusted from 0.17mV to 6.85 mV under steerable conditions. The maximum short circuit current reached 0.689 mA and maximum power density reached 1.33 mW·m-2. To deeply verify the application potential of the flexible electromagnetic sensors, an intelligent jacket, which was sewn with flexible magnetic film and copper coils was designed. It is capable of monitoring motion signals and distinguishing the motion state, proving that the biodegradable flexible electromagnetic sensor is promising to be utilized in wearable field as a kind of eco-friendly flexible sensor.
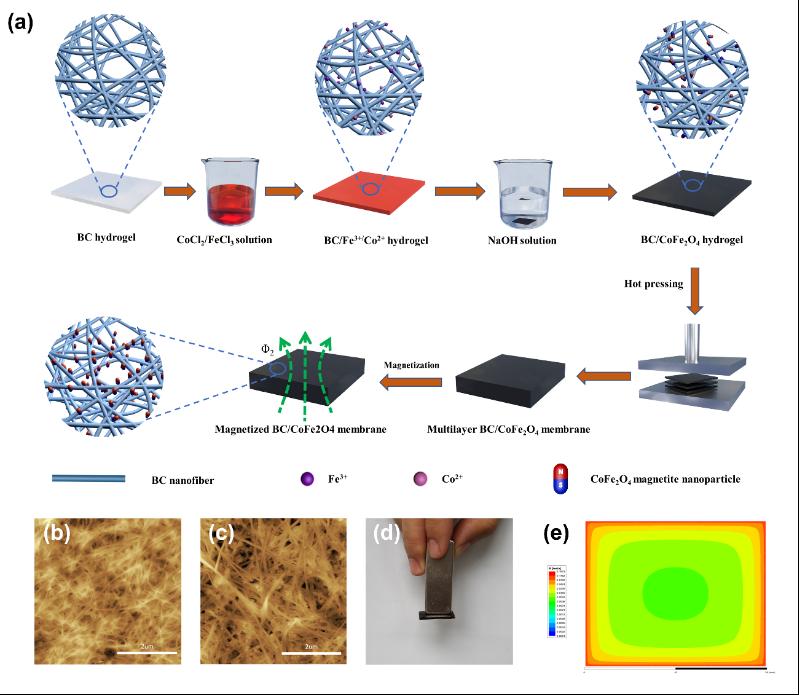
Figure 1. (a) The preparation process schematic of flexible magnetic film. (b) The surface AFM image of fiber network structure of pure BC. (c) The surface AFM image of composited magnetic film with CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. (d) The flexible magnetic film was attached to a block of iron handily. (e) The magnetic flux density pattern of the flexible magnetic film.
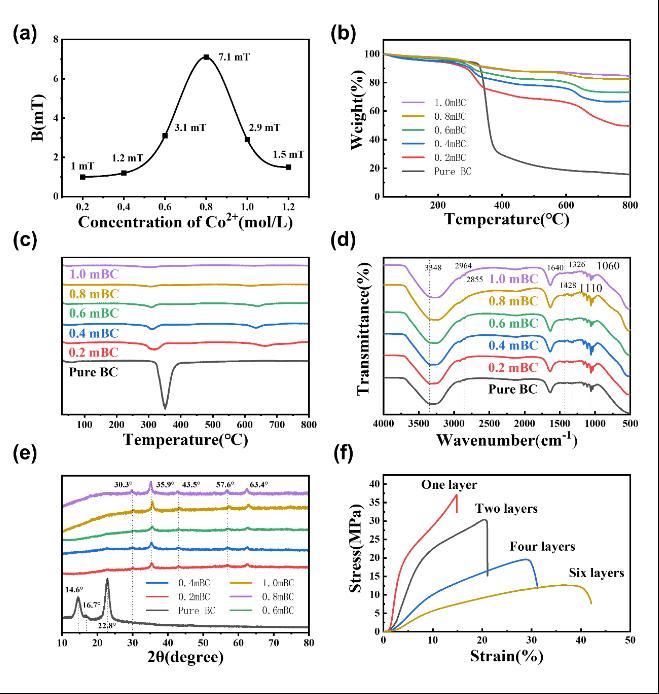
Figure 2. (a) Diagram of magnetic flux density of flexible magnetic films fabricated under different metal ion concentrations. (b) TG and (c) DTG curves of flexible magnetic films. (d) FT-IR spectra and (e) XRD patterns of flexible magnetic films. (f) Stress-strain curves of composited magnetic films hot-pressed with different numbers of layer.
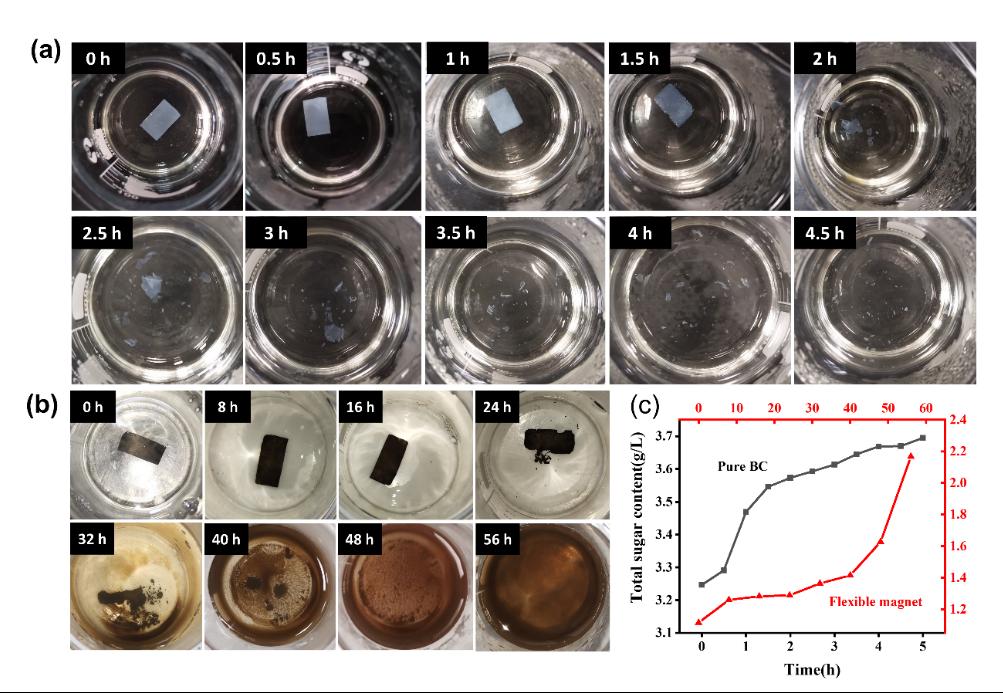
Figure 3. (a) Photos of pure BC during degradation process within 4.5h. (b) Photos of flexible magnetic film during the degradation process within 56h. (c) Total sugar content of pure BC and flexible magnetic film during the whole degradation process. Red curve belongs to flexible magnetic film and black curve belongs to pure BC.
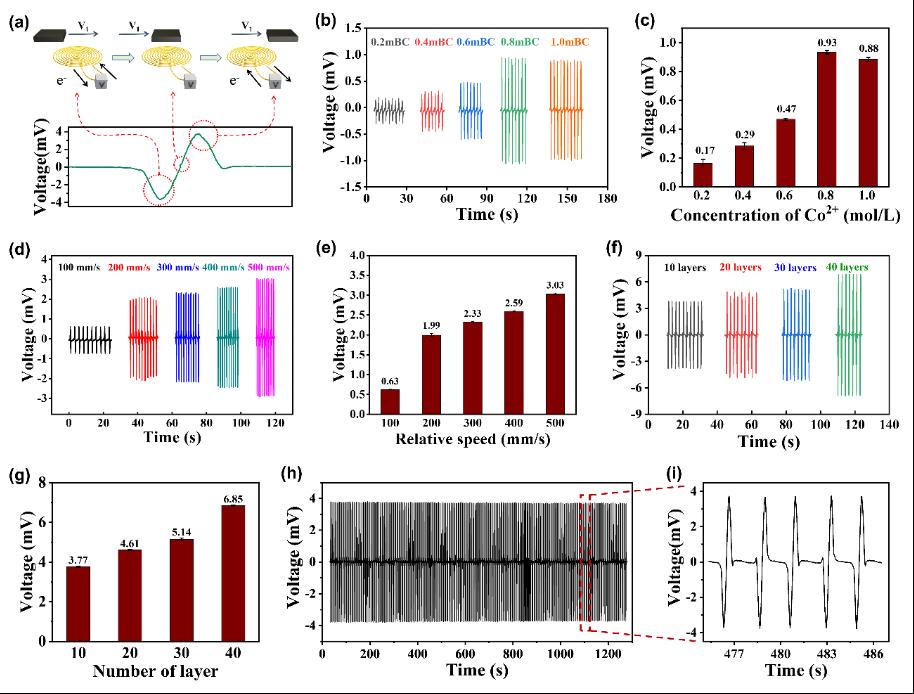
Figure 4. (a) Schematic diagram of induced voltage generation. (b) The sensor signals of flexible magnetic films prepared under different concentrations. (c) The peak voltage of signals in (b). (d) The sensor signals of flexible magnetic films in different relative speed. (e) The peak voltage of signals in (d). (f) The sensor signal of flexible magnetic films with different layers. (g) The peak voltage of signals in (f). (h) The motion signal over 1000 cycles. (i) A section of signals after 1000 cycles from (h).
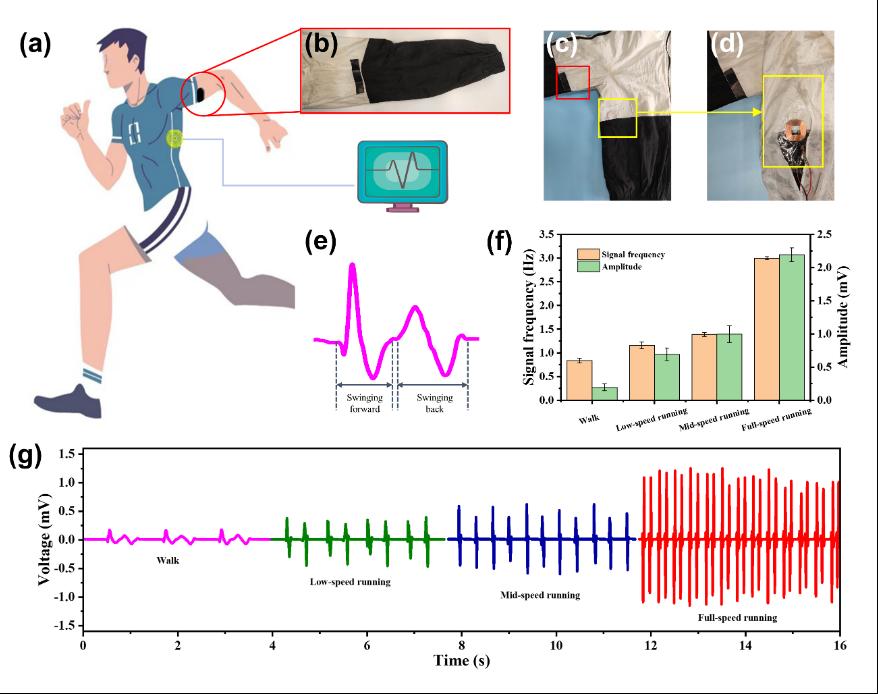
Figure 5. (a) Schematic diagram of intelligent jacket. (b) Flexible magnetic film was sewn at the elbows of the jacket sleeves. (c) The relative position of flexible magnetic film and the copper coils. Red box is flexible magnetic film and yellow box is copper coils. (d) The copper coils were sewn in the interlayer of the jacket for invisibility. (e) The wave of a whole motion cycle in the walk (0.8 m/s) mode with two distinguish and intact waves with different directions. (f) The relation between amplitude and frequency with motion speed in each motion mode. (g) The sensor signal in four motion modes: walk (0.8 m/s), low-speed running (2 m/s), mid-speed running (3.5 m/s) and full-speed running (6.5 m/s).
该工作由华中科技大学生命科学与技术学院杨光教授团队与材料科学与工程学院苏彬教授团队共同合作完成。论文共同第一作者为华中科技大学博士生陈坤、华中科技大学硕士李一凡、华中科技大学杜卓林博士。华中科技大学杨光教授、华中科技大学苏彬教授、华中科技大学石志军博士为该文章的共同通讯作者。
该工作得到了金砖国家科技创新框架计划(3rd call 2019)、国家重点研发计划(批准号 2018YFE0123700)、国家自然科学基金(批准号 51973076 和 52073031)、国家纺织新材料与先进加工技术重点实验室(批准号:FZ2021005)和中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(批准号:2020kfyXJJS035、WUT2018IVB006、Z191100001119047)等的支持。
论文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2211285522008187
论文引用:Kun Chen, Yifan Li, Zhuolin Du, Sanming Hu, Jianyu Huang, Zhijun Shi, Bin Su, Guang Yang,CoFe2O4 Embedded Bacterial Cellulose for Flexible, Biodegradable, and Self-powered Electromagnetic Sensor,Nano Energy,2022,107740,ISSN 2211-2855, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107740.